In this digital age, it is very crucial for businesses to have a robust online presence if they want to stand out in the competitive market. Web development plays a key role in this digital evolution, breathing life into websites and making them dynamic and engaging. Web development encompasses a range of tasks, from designing a visually appealing interface to ensuring seamless functionality. Now, let’s learn more about what web development process is and also explore its various stages which help build a successful and impactful online presence. Each stage, thoughtfully executed, transforms a static web page into a dynamic and engaging digital experience.
What is Web Development?
Web development, the fusion of art and science, entails building and nurturing websites. It takes on a versatile approach, seamlessly blending design, coding, and functionality to craft an immersive online experience. In an era where businesses depend more on the internet to engage with their audience, the significance of web development has grown exponentially.
Read More: The Impact of Professional Website Development: Exploring Its Top 10 Benefits
Front End & Back End Web Development
Web development, a multifaceted discipline, branches into two primary categories: Front End Development and Back End Development.
Front End Development
Front End Development, also known as client-side development, revolves around the elements of a website that users interact with directly. This involves shaping the design, layout, and the overall visual appeal of the site. Front-end developers employ languages like HTML, CSS, and JavaScript to craft a captivating user interface, captivating visitors and ensuring a smooth browsing experience.
Back End Development
On the flip side, Back End Development, or server-side development, delves into the behind-the-scenes functionality powering the website. Back end developers work on the server, database, and application, ensuring that everything runs smoothly. They focus on server configuration, database management, and application logic, enabling the seamless functioning of the website.
Understanding the distinction between Front End and Back End Development is pivotal for businesses venturing into the web development journey. The harmonious integration of both results in a website that not only looks visually appealing but also performs optimally, delivering a superior user experience.
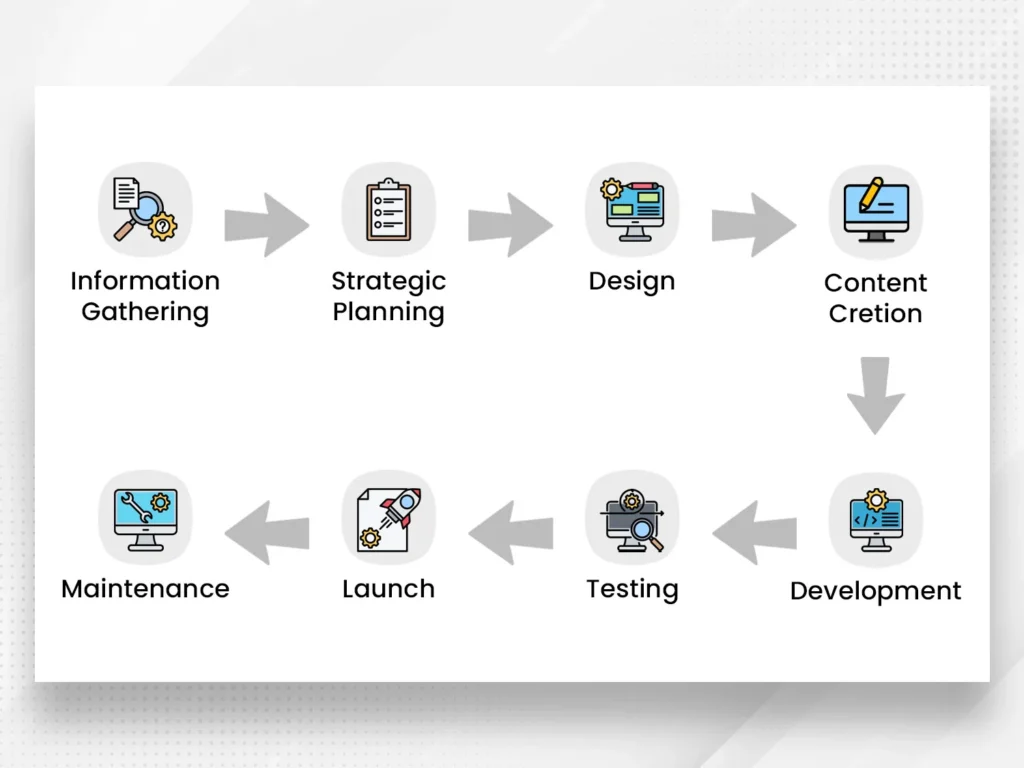
Stages of Web Development Process
The “Stages of Web Development Process” act as a meticulous guide, navigating through eight essential phases that build and maintain a successful website. Picture it as a roadmap, systematically leading from the initial idea to continuous enhancements.
Stage 1: Gathering Information
This initial stage sets the tone for the entire web development journey. Imagine having a detailed roadmap before a journey—knowing the starting point, destination, and all landmarks in between ensures a fulfilling experience. Gathering information here is critical as it forms the basis for every subsequent decision in the web development process.
Key Aspects of Gathering Information:
- Target Audience: Understanding who the website is for is paramount. The design, content, and functionality should cater to the intended audience, shaped by factors like age, community, gender, and preferences.
- Objective and Purpose: Identifying basic and advanced functionalities is crucial, shaping the entire development process based on whether it’s an e-commerce site, a blog, or a portfolio. Understanding what the website is expected to do influences the entire development process.
- Client’s Expectations: Grasping the client’s vision for design, functionality, and overall user experience ensures the end product aligns seamlessly with their goals.
Stage 2: Strategic Planning
Every type of website necessitates a unique roadmap. An e-commerce site may prioritize seamless transactions, while a blog focuses on engaging content delivery. Strategic planning tailors the roadmap based on information gathered, ensuring each element serves its purpose effectively.
Key Aspects of Strategic Planning:
- Website Architecture: This involves deciding how pages and content will be organized, ensuring an intuitive and user-friendly experience.
- Navigation Flow: Ensuring a smooth navigation flow is paramount. Strategic planning determines how users move through the site, ensuring a logical and effortless journey.
- Content Strategy: Outlining the content strategy involves deciding what information will be presented, how it will be structured, and how it aligns with the overall objectives.
- Functionality Features: Based on planned functionalities identified in the gathering information stage, strategic planning decides on features like contact forms, e-commerce capabilities, and interactive elements.
Stage 3: Design
This is the creative hub of web development – the Design stage. This is where the website’s visual elements come to life with precision and flair. Designers focus on aesthetics, user experience and representing the brand visually, ensuring that colors, fonts, and layout choices resonate with the strategic plan.
Key Aspects of Design:
- Brand Representation: Just as a logo serves as the face of a company, colors, fonts, and layout choices play a crucial role in visually representing the brand identity established in earlier stages.
- User Experience (UX) Design: Crafting an exceptional user experience ensures intuitive and satisfying interactions throughout the website.
- Mockups and Prototypes: Designers create visual representations, allowing clients to preview the website before it goes live, aligning with their vision.
Stage 4: Content Creation
This stage often overlaps with other phases of the web development process and may continue even after the post-launch period. Content is the voice of the website, impacting user perception and interaction. Just as a captivating story keeps readers hooked, compelling content keeps website visitors engaged and encourages them to return.
Key Aspects of Content Creation:
- Clarity and Simplicity: Content should be clear and easy to understand, avoiding complex language for effortless navigation.
- Relevance to Audience: Understanding the target audience’s interests and needs is crucial. Content should address their queries, provide valuable insights, and resonate with their preferences.
- Consistency: Consistency in tone, style, and messaging is vital for building a brand identity, creating a cohesive and recognizable brand voice.
Read More: 10 Key Skills for Mastering the Art of Content Writing
Stage 5: Development
This stage is the powerhouse of web creation – the Development stage. Stage 3, Design, is where the visual narrative is crafted, while Stage 5, Development, breathes life into the digital blueprint. This collaborative effort between designers and developers ensures your final product isn’t just a visual treat but a seamless and fully functional experience. Every design element, from images to buttons, is meticulously coded, promising a seamless and responsive user experience.
Key Aspects of Development:
- Bringing Mockups to Life: Developers transform static designs into a dynamic, operational website, ensuring a smooth and interactive user journey.
- Front End Development: With the help of languages like HTML, CSS, and JavaScript, front end developers craft the visual components, ensuring perfect alignment with the design and delivering an interface that captivates users.
- Back End Development: Operating behind the scenes, Back End Developers manage databases, handle user authentication, and ensure overall functionality. They focus on server configuration, database management, and application logic, enabling the smooth functioning of the website.
Front end and back end developers work in harmony to produce a website that not only looks appealing but also functions according to the plan.
Stage 6: Testing
Testing is the quality control checkpoint of the web development journey. Developers and testers rigorously assess the website to ensure that content is accurate, functions work as intended, and navigation is user-friendly.
Key Aspects of Testing:
- Content Accuracy: Ensuring that the content is accurate is paramount. Inaccurate content can misguide users and undermine the credibility of the website.
- Functional Integrity: Testing assesses the seamless operation of all functionalities, ensuring users can interact without encountering technical glitches.
- Cross-Browser Compatibility: Ensuring the website displays and functions correctly on various popular browsers like Chrome, Firefox, Safari is vital.
- Responsiveness: Testing and ensuring that the website looks and functions properly on every device is very important.
- Identifying and Fixing Issues: Testing helps identify and address issues, bugs, or inconsistencies early for a smooth launch and positive user experience.
Stage 7: Launch
The launch marks the point where the website goes live, and users can interact with the digital space.
Key Aspects of the Launch:
- Domain Configuration: Configuring the domain ensures users access the website through a recognizable and user-friendly web address.
- Hosting Environment: Choosing a reliable hosting environment is crucial for the website’s accessibility and responsiveness.
- SSL Certificates: Implementing SSL certificates ensures secure communication, encrypting data transmitted between users and the website.
- Final Checks: Even after extensive testing, a final round of checks verifies that all functionalities work correctly and content displays as intended.
- Security Measures: Implementing security measures on the server, like firewalls and encryption protocols, is essential to safeguard the website and user data.
Stage 8: Maintenance
The final stage involves continuous maintenance to ensure the website remains in optimal condition after its grand launch. Regular updates, bug fixes, and security checks are the tools that ensure the website stays reliable, secure, and user-friendly.
Key Aspects of Maintenance:
Regular Updates: Keeping the website’s software, plugins, and frameworks updated is crucial for staying current with technology trends and security patches.
- Bug Fixes: Identifying and fixing bugs that may arise post-launch is essential for maintaining a seamless user experience.
- Security Checks: Regular security audits and checks protect the website from potential threats, implementing measures to stay vigilant against emerging risks.
- Regular Backups: Backing up website data regularly ensures data restoration in case of unforeseen issues.
- SEO Benefits: Search engines favor websites that are regularly updated and secure. Ongoing maintenance contributes to improved search engine rankings, enhancing the website’s visibility.